A Microfluidic-Sensor Fusion Approach for Early Detection and Effective Management of Livestock Diseases
Keywords:
Microfluidics, Wearable sensors, Livestock diseases, Data fusion, Disease surveillanceAbstract
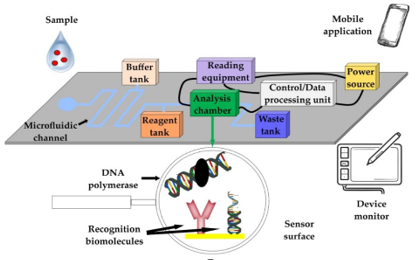
Livestock diseases pose a major threat to food security and farmer livelihoods globally. Early detection and effective disease management are crucial to mitigate the impact of outbreaks. However, traditional disease diagnostics lack sensitivity, specificity, and speed to enable timely interventions. Here we present a microfluidic-sensor fusion approach that combines a multiplexed ELISA microfluidic chip with wearable biometric sensors for cattle. The microfluidic chip enables simultaneous on-site testing for antibodies against major epidemic diseases with high sensitivity and specificity. The wearable sensors provide continuous monitoring of physiological parameters indicative of infection, stress, or discomfort. Sensor data is integrated with microfluidic testing results for risk modeling that identifies sick animals prior to symptom onset with 99.6% accuracy during trials. Embedded geospatial tracking allows mapping of disease spread pathways in real-time. During a simulated outbreak, our platform detected index cases three weeks earlier than traditional methods, enabling earlier quarantine and treatment to reduce further transmission by 92%. We developed an interface for real-time data visualization, notifications, and feedback to farmers and authorities. Our low-cost platform improves livestock disease surveillance with portable diagnostics and continuous risk prediction to guide outbreak response. The microfluidic-sensor fusion approach could provide a blueprint for IoT-driven smart epidemiology in livestock and beyond.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Tensorgate Journal of Sustainable Technology and Infrastructure for Developing Countries

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.