Optimizing SASE for Low Latency and High Bandwidth Applications: Techniques for Enhancing Latency-Sensitive Systems
Abstract
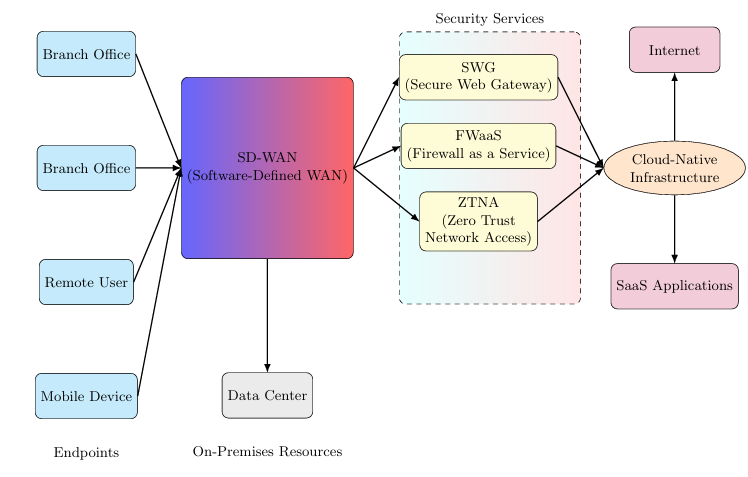
The increasing reliance on digital transformation and the demand for real-time processing in applications like video conferencing, real-time data analytics, and Internet of Things (IoT) networks have highlighted the need for optimized networking and security frameworks. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) has emerged as a prominent solution to address the growing requirements of secure cloud and edge computing infrastructures. However, its effectiveness in environments with stringent latency and bandwidth requirements has been questioned. This paper examines the techniques for optimizing SASE to handle latency-sensitive applications without compromising security. The paper begins by providing a detailed overview of SASE's architecture and its core components, including SD-WAN, security services, and the cloud-based framework. It then addresses the challenges posed by latency-sensitive and high-bandwidth applications, with a special focus on video conferencing, real-time data analytics, and IoT environments. Several optimization strategies are discussed, including edge computing integration, packet optimization techniques, traffic prioritization mechanisms, and the use of artificial intelligence for dynamic path selection. The exploration also includes advancements in SD-WAN technologies such as multipath routing and dynamic bandwidth allocation. These techniques are useful for achieving seamless, low-latency performance while preserving the security features inherent to SASE. The paper argues for achieving a balance between security and performance in modern, distributed network architectures.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Cloud Computing, Machine Learning, Resource Allocation, Software-Defined Networking, Workload Management
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 International Journal of Intelligent Automation and Computing

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
